Product Applications & Antenna Types
All wireless applications need antennas for transmission and reception of free-space waves. This website will state a few popular examples of applications and what kind of antennas can be used.
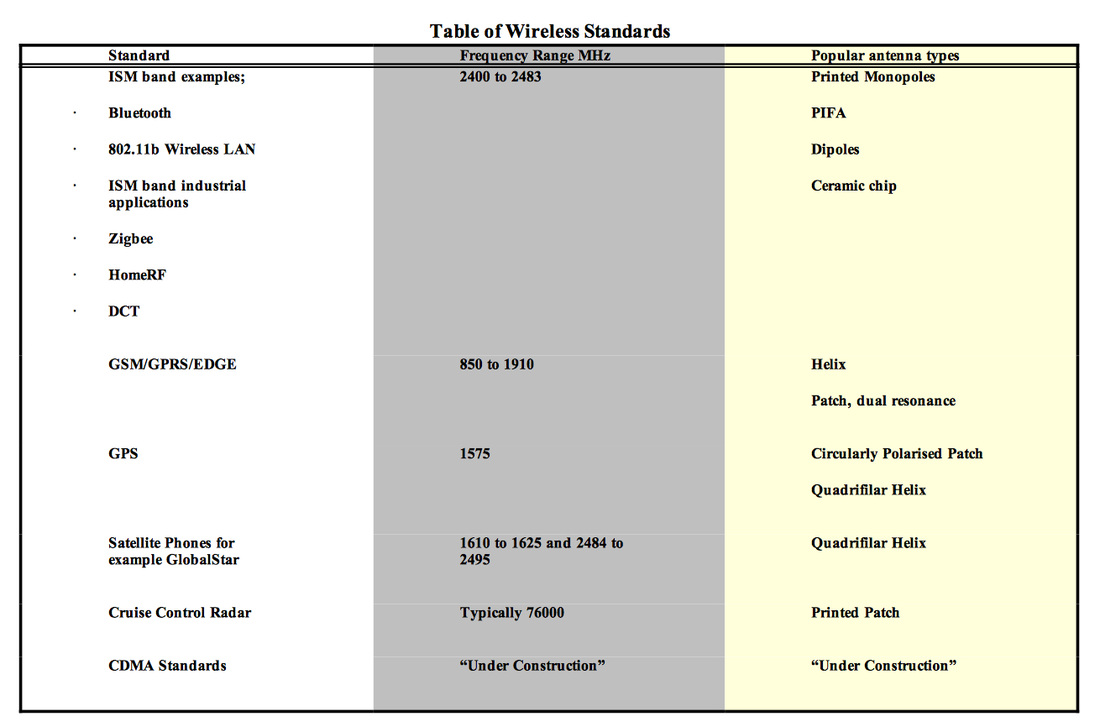
Most of the 2.4GHz ISM band applications use either printed antennas or ceramic chip and rarely dipoles or helix. This is due to the fact that they are cheap and relatively easy to implement for these types of low power applications.
Most GSM phones use patch antennas and some still use helix or monopoles. Patch antennas are normally in the form of an elevated printed patch that is etched onto a low dielectric polymer, which is then attached to the main PCB of the phone.
GPS antennas are either in the form of a circularly polarised patch or quadrifilar helix. Circular polarisation is used for satellite communication due to its low propagation loss.
Satellite phones for example Globalstar or ACeS also use quadrifilar helix antennas since they offer excellent radiation patterns suited for low ground noise reception of weak signals. They also offer high gain towards the zenith.
Automotive cruise control radar generally uses three rectangular printed patch antennas, which are only a few millimetres across due to the very high frequencies being used. The three beams are focused by a dielectric lens to track the cars in front of the vehicle.
Popular Types
Some of the popular types are shown in the table below, these are;
All wireless applications need antennas for transmission and reception of free-space waves. This website will state a few popular examples of applications and what kind of antennas can be used.
Most of the 2.4GHz ISM band applications use either printed antennas or ceramic chip and rarely dipoles or helix. This is due to the fact that they are cheap and relatively easy to implement for these types of low power applications.
Most GSM phones use patch antennas and some still use helix or monopoles. Patch antennas are normally in the form of an elevated printed patch that is etched onto a low dielectric polymer, which is then attached to the main PCB of the phone.
GPS antennas are either in the form of a circularly polarised patch or quadrifilar helix. Circular polarisation is used for satellite communication due to its low propagation loss.
Satellite phones for example Globalstar or ACeS also use quadrifilar helix antennas since they offer excellent radiation patterns suited for low ground noise reception of weak signals. They also offer high gain towards the zenith.
Automotive cruise control radar generally uses three rectangular printed patch antennas, which are only a few millimetres across due to the very high frequencies being used. The three beams are focused by a dielectric lens to track the cars in front of the vehicle.
Popular Types
Some of the popular types are shown in the table below, these are;
- Monopole
- Dipole
- PIFA
- Ceramic Chip
- Helix
- Patch
- Quadrifilar Helix